Introduction
E-cigarette was invented in 2003 by Chinese pharmacist Hon Lik, who initially developed the device to serve as an alternative to conventional smoking. Despite their widespread popularity, there remains limited knowledge about their health implications. Opinions regarding the potential risks and benefits of e-cigarette use vary significantly among the public, e-cigarette users, healthcare providers, and the public health community. One area of debate is whether e-cigarette use entails a reduced risk of addiction in comparison to conventional tobacco cigarettes. Additionally, questions persist about the potential dangers of e-cigarettes, stemming from the exposure to potentially harmful substances in their emissions, particularly among individuals who are new to tobacco use, such as adolescents and young adults. Furthermore, fears have been made that e-cigarettes will encourage young people to start smoking traditional tobacco cigarettes.

According to the report by CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention), published on June 23, 2023, between April 2022 and March 2023, there were 7,043 reported cases of e-cigarette exposure, a 32% increase. Most cases (87.8%) involved children under 5 years old. Inhalation (61.0%) and ingestion (40.0%) were the primary routes of exposure. Hospital admission was necessary in 0.6% of cases, with one reported death (suspected suicide). Roughly half of the cases had minor effects or no reported effects, and follow-up information was missing in 50.9% of cases.
What is an E-Cigarette?
E-cigarettes, or electronic cigarettes, are electronic devices that simulate the act of smoking by vaporizing a liquid solution. E-cigarettes consist of a battery, a heating element (atomizer or coil), and a reservoir to hold the liquid, known as e-liquid or vape juice. E-cigarettes can come in various shapes, sizes, and designs. Some resemble traditional cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, while others resemble pens, USB sticks, or other everyday objects. The e-liquid used in e-cigarettes typically consists of a mixture of propylene glycol and/or vegetable glycerin, flavorings, and nicotine. However, nicotine-free e-liquids are also available for those who do not wish to consume nicotine.
How Does E-Cigarette Work?
E-cigarettes, also known as electronic cigarettes or vaping devices, consist of several key components that work together to deliver a vaporized aerosol to users. These components include:
Battery: The battery powers the e-cigarette device. It is usually rechargeable and provides the energy needed to heat the e-liquid.
Atomizer: The atomizer is responsible for heating the e-liquid and turning it into vapor. It contains a heating coil that heats up when the battery is activated.
E-Liquid (E-Juice): This is the liquid solution that is vaporized to create the aerosol. E-liquids typically consist of a mixture of propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, flavorings, and nicotine (optional).
Cartridge or Tank: The cartridge or tank holds the e-liquid and is attached to the atomizer. Some devices use disposable cartridges, while others have refillable tanks.
Heating Coil: The heating coil is part of the atomizer and is responsible for vaporizing the e-liquid. When the coil is heated, it turns the e-liquid into vapor.
Airflow Sensor or Button: Some e-cigarettes have an automatic airflow sensor that detects when the user takes a puff and activates the heating coil. Others have a button that the user presses to activate the device.
Mouthpiece: The mouthpiece is where the user inhales the vapor. It is usually made of plastic or metal and is attached to the top of the e-cigarette.
LED Indicator: Many e-cigarettes have an LED light that simulates the glow of a burning cigarette. The light may also indicate the device's status, such as battery level or activation.
Control Circuitry: In more advanced devices, control circuitry regulates various functions of the e-cigarette, such as temperature control and power output.
These components work together to create the vapor that users inhale, mimicking the experience of smoking traditional cigarettes without the combustion and tobacco-related chemicals.

Image Source: https://sites.psu.edu/mackenziemoon/2015/01/
Evolution of E-Cigarette
Generation | Description | Features |
|---|---|---|
 First Generation | These e-cigarettes were designed to resemble traditional cigarettes. They were often disposable and had a similar size and shape. First-generation e-cigarettes typically had automatic batteries activated when the user took a puff. They had limited battery life and low vapor production. |
|
 Second Generation | The second generation introduced vape pens, which were larger and more powerful than first-generation e-cigarettes. They featured manual batteries with a button to activate the heating element, allowing users to control the vapor production. These devices often had refillable tanks or cartridges, offering more customization options. |
|
 Third Generation | Third-generation e-cigarettes, also known as advanced personal vaporizers (APVs) or mods, brought significant advancements to the vaping experience. These devices featured larger batteries, variable voltage/wattage settings, and advanced safety features. They allowed users to adjust power output, and temperature control, and use different atomizers and tanks. |
|
 Fourth Generation | Fourth-generation e-cigarettes introduced pod systems, which became increasingly popular due to their simplicity and convenience. These devices used pre-filled or refillable pods that contained both the e-liquid and the heating element. Pod systems were smaller and more portable than previous generations and often had a draw-activated mechanism. They offered a more user-friendly experience for beginners. |
|
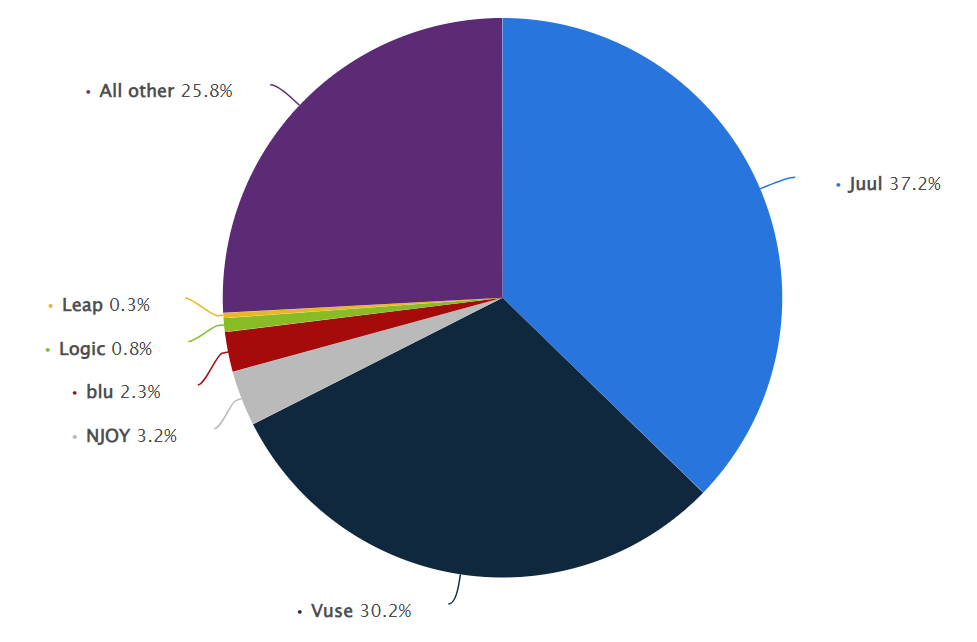
Market Share by Brand in the U.S. E-Cigarette Sales (2022)
In 2022, Juul secured its position as the dominant e-cigarette brand in the United States, commanding a substantial 37 percent share of the market. Following closely was Vuse, holding a notable 30 percent market share. Notably, Vuse is produced by Reynolds American Tobacco, while Juul burst onto the U.S. e-cigarette scene in 2015 as a startup under Pax Labs. However, it rapidly outpaced long-standing tobacco industry giants to claim the top spot. In 2018, Altria Group acquired a significant 35 percent stake in Juul, further solidifying its market presence.
The rise of electronic cigarettes in the U.S. can be attributed to their emergence as an alternative to traditional combustible tobacco products, particularly as a growing number of smokers sought ways to quit. Notably, the sales of conventional cigarettes have been consistently dwindling over the years. This shift towards smokeless alternatives led to electronic cigarette sales reaching an impressive 3.8 billion U.S. dollars in 2018 across various retail channels in the United States.
Patent Analysis

While China has emerged as a leader in the number of patents in the e-cigarette market, the United States also holds a significant presence in this field. Here is a comparison of the two countries:
Patent Quantity: China has a higher number of patents in the e-cigarette market compared to the United States. Chinese companies have been actively filing patents to protect their innovations, taking advantage of the country's manufacturing capabilities and market demand.
Technological Innovation: Both China and the United States have contributed to technological advancements in the e-cigarette industry. Chinese companies have focused on hardware development, manufacturing efficiency, and cost-effective production. In contrast, American companies have emphasized product design, user experience, and advanced vaping technologies.
Market Influence: China's dominance in e-cigarette manufacturing and exporting has given it a significant market influence. Chinese-made e-cigarettes are widely distributed globally, including in the United States. However, the United States has a strong domestic market and has been a hub for e-cigarette innovation and the development of new vaping technologies.
Top Patent Assignees

Huizhou Kimree Technology Co., Ltd. is a Chinese company that designs and manufactures e-cigarettes and related products. The company was founded in 2006 and is headquartered in Huizhou, Guangdong, China. Kimree has a global presence with offices and distributors in the United States, Europe, and Asia. It does not have a significant market share in the global e-cigarette market. According to the market research firm Euromonitor International, the company's market share is estimated to be around 1%. The company has the greatest number of patents in the e-cigarette industry because the company is very focused on research and development. Kimree has filed for over 1,500 patents in the e-cigarette space, more than any other company in the world.
Kimree's patents cover a wide range of e-cigarette technologies, including:
Vaporizers: Kimree has patented a number of different vaporizer designs, including pod systems, disposables, and mods.
Nicotine Cartridges: Kimree has patented a number of different nicotine cartridges, including cartridges with different nicotine strengths and flavors.
E-liquids: Kimree has patented a number of different e-liquid formulations, including e-liquids with different nicotine strengths and flavors.
Other E-cigarette Components: Kimree has also patented a number of other e-cigarette components, such as batteries, chargers, and mouthpieces.
The prevalence of e-cigarette patent holder companies in China can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, China has a well-established manufacturing ecosystem with advanced technology and resources, making it conducive for producing e-cigarettes. This has led to the emergence of numerous Chinese manufacturers specializing in e-cigarettes. Additionally, China's relatively lenient intellectual property protection policies and lower patent registration costs might encourage these companies to secure patents. However, having a large number of patents does not necessarily translate to a higher market share. Market dynamics, consumer preferences, marketing strategies, and regulatory environments can all influence a company's market position. Therefore, while these companies hold significant patents, various factors could contribute to their relatively smaller market share compared to other players.
Patent Filing Trend for the Last 10 Years

The decline in e-cigarette patent filings post-2019 can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, increased regulatory uncertainty, especially in the United States and other regions, led to stricter rules and deterred companies from investing in new e-cigarette technologies. Secondly, the market saw saturation and reduced innovation as numerous patents covered various aspects of e-cigarette tech. The dominance of pod-based systems, like JUUL, further consolidated the market. Public health concerns, including vaping-related lung injuries, and economic factors also influenced companies' patent strategies, impacting the industry's patent landscape.
Conclusion
E-cigarettes have become a popular and diverse product category, delivering nicotine and additives through inhaled aerosol. Concerns arise regarding their use among youth and young adults, surpassing traditional cigarettes in popularity. E-cigarette use is linked to other tobacco product use and poses risks to youth, pregnant women, and fetuses. The aerosol contains harmful constituents, including nicotine, which can lead to addiction and harm the developing adolescent brain. E-cigarette marketing often targets youth with appealing flavors and various media channels. Actions at different levels, such as implementing smoke-free policies, restricting youth access, regulating marketing, and educational initiatives, can address youth and young adult e-cigarette use.
References
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/216550#recent_research
https://www.podsalt.com/blog/post/how-do-e-cigarettes-work-all-you-need-to-know
https://www.lung.org/quit-smoking/e-cigarettes-vaping/whats-in-an-e-cigarette
https://science.howstuffworks.com/innovation/everyday-innovations/electronic-cigarette.htm
https://dailygazette.com/2016/03/06/exploding-e-cigarettes-send-users-hospital-gruesom/
https://science.howstuffworks.com/innovation/everyday-innovations/electronic-cigarette.htm
https://www.fda.gov/tobacco-products/retail-sales-tobacco-products/tobacco-21
https://www.fda.gov/news-events/fda-voices/how-fda-regulating-e-cigarettes
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanpub/article/PIIS2468-2667(20)30063-3/fulltext

Comentários